What injury occurred with an elderly woman falling onto an outstretched arm?
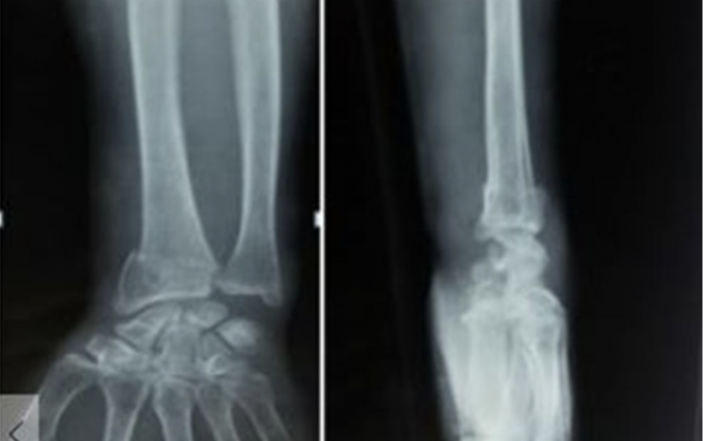
A 72-year-old woman tripped and fell on an outstretched arm, sustaining the fracture depicted in the X-ray below.

Which of the following nerve injuries is most commonly associated with this fracture pattern?
- A. Anterior interosseous nerve
- B. Axillary nerve
- C. Median nerve
- D. Radial nerve
- E. Ulnar nerve
Correct answer: C. Median nerve
The fracture shown is a Colles’ fracture, or dorsally displaced distal radius fracture. It is commonly associated with median nerve injury and/or development of carpal tunnel syndrome (compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel). The nerve may be stretched due to wrist hyperextension at the time of injury, compressed by hematoma or bone fragment, or the carpal tunnel compressed if the wrist is splinted in too much flexion.
Nerve function can be assessed by having the patient hold the tip of the thumb against the tip of the pinky finger and resist the examiner pulling these apart. This tests the opponens pollicis muscle. This is innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve, which branches off distal to the carpal tunnel. Median nerve function should be tested before and after fracture reduction is performed.
Incorrect answer choices:
The anterior interosseous nerve (Choice A) is a deep motor branch of the median nerve, which can be injured from a supracondylar humerus fracture. It can be tested by assessing the ability to flex the thumb IP joint, to make an “OK” sign, or to pinch a piece of paper between the thumb and forefinger.
The axillary nerve (Choice B) may be injured in shoulder dislocations or proximal humerus fractures. It can be tested by assessing sensation over the lateral deltoid, or deltoid muscle activation with shoulder abduction past 18 degrees (the first 18 degrees of abduction are performed by the supraspinatus).
The radial nerve (Choice D), also known as the great extensor, may be injured with a humeral shaft fracture. Radial nerve function can be assessed by testing strength of thumb extension and sensation on the dorsum of the thumb.
The ulnar nerve (Choice E) can be injured with fractures around the elbow or, less commonly, the forearm. Ulnar nerve function can be assessed by testing the strength of finger abduction (dorsal interosseous muscles).