Patient presents with soreness, but which approach is best?
Question:
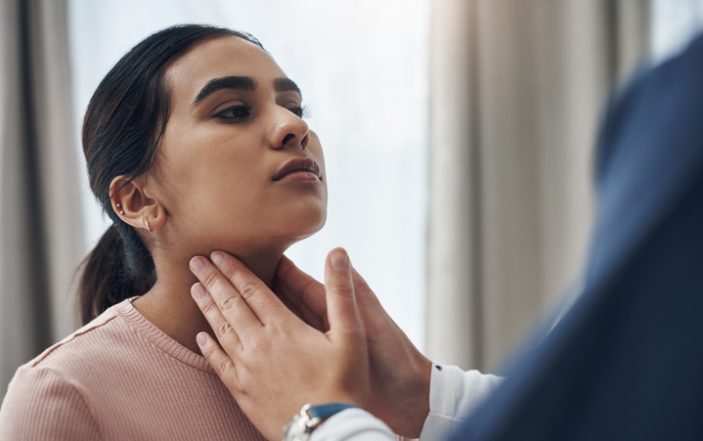
A 16-year-old male presents to the emergency department complaining of two days of sore throat without fever. He denies cough. Exam reveals tender submandibular and anterior cervical lymph nodes. Oral exam is as shown.

Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- Amoxicillin 500 mg orally twice daily for 10 days
- Dexamethasone 8 mg orally once
- Incision and drainage
- Penicillin G 1.2 million units intramuscularly once
- Rapid streptococcal antigen testing
Correct answer: E. Rapid streptococcal antigen testing
This patient presents with 3 points based on Modified Centor Criteria, so rapid streptococcal antigen testing should be performed. GABHS pharyngitis is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis, comprising approximately 5-15% of all cases of pharyngitis in adults and 20% to 30% of cases in children.
Complications of GABHS pharyngitis include development of peritonsillar abscess, cervical lymphadenitis, mastoiditis, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever, although the latter is now uncommon in developed countries.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommend having two or more Centor criteria as a threshold for obtaining rapid strep testing. It is not recommended to treat based on clinical features alone. The IDSA and American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines advocate against treating with just the Modified Centor Criteria, even if high probability (4+ points) because many people who receive 4 and 5 points on the criteria still return negative formal testing results (approximately 1/3).

Many years ago, the CDC agreed with the American College of Physicians (ACP) guidelines (2003) in that it was OK to consider giving antibiotics for 4 points or more. The ACP previously advocated for treating just based on Centor criteria, but that is not the case at this point.
In this vignette the debate is null since the patient receives 3 points. If testing returns positive, a single dose of IM penicillin G, or ten days of oral penicillin V or amoxicillin are the recommended antibiotic regimens.
Incorrect answer choices:
While amoxicillin (Choice A) is an appropriate antibiotic regimen, treatment for strep should only be initiated if rapid testing returns positive. Oral antibiotic regimens for strep pharyngitis are for 10 days, except azithromycin (five days).
Penicillin IM (Choice D) is also an appropriate antibiotic regimen for Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS). It is true that the rapid strep tests are only moderately sensitive and specific, but these are current guideline recommendations as part of antibiotic stewardship.
Corticosteroids (Choice B) are sometimes given as adjunctive therapy to patients with pharyngitis, but it is important to first exclude GABHS as the cause of symptoms.
Although tonsils are sometimes asymmetric in strep pharyngitis, this patient has not developed a peritonsillar abscess, so I&D would not be the right course of management (Choice C).
References:
Shulman S, Bisno A et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2012; 55(10), e86-e102 https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis629
Hartman N. Chapter 246.Neck and Upper Airway. In: Tintinalli JE, Stapczynski JS, Ma OJ, et al. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Professional; 2016.




2 Comments
One complication that is worth mentioning, although rare, is PANDA. Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder Associated with Strep infx. This is a weird bird, but very dramatic. Typically young kid or teen, with sudden onset neuropsych complaints. It can present with OCD, tics, behavior changes all the way to full psychosis. Initial tests are typically normal, maybe some inflammatory markers are elevated. Pt or parents may not even remember the sore throat from 2-3 wks ago. It is due to cross reactivity from the bug antigens with the basal ganglia. Tx is plasmapheresis + IVIG + PNC for ongoing infection. ✌
I agree with the case summary and recommendations. This approach is consistent with CDC and IDSA guidelines. However, there are many opinions suggesting no testing, no treatment or empiric steroids. As examples https://rebelem.com/patients-strep-throat-need-treated-antibiotics/ https://rebelem.com/corticosteroids-in-pharyngitis-systematic-review-meta-analysis/
Many have interpreted as no testing, no antibiotics and offer steroids. Longer debate about this approach.