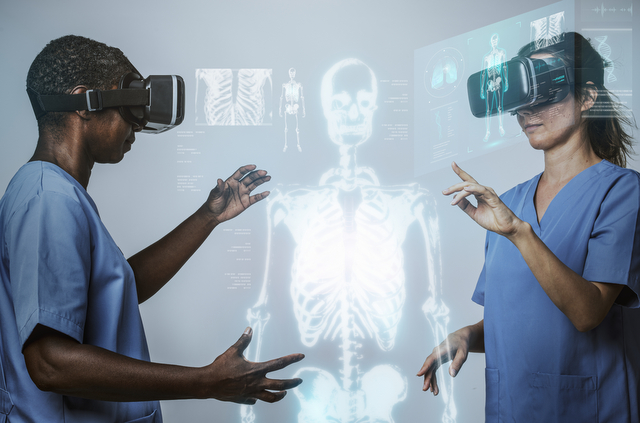
In the medical industry, training is one of the most important aspects of a doctor’s career. Since doctors hold their patients’ lives in their hands, they must be well-trained and prepared to handle any number of situations that come their way, so any tool that can be used to improve training for doctors could save lives.
How VR and AR are transforming medical training
What if we told you that a technology that was once used for little more than gaming has now become one of the most influential tools in the process of medical training?
In recent years, the use cases of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have expanded beyond entertainment. Professionals in various industries, including healthcare, have seen VR and AR’s potential for training and onboarding. These technologies allow learners to get experience in a low stakes but hands-on and realistic virtual environment, creating a much more effective training experience. Indeed, numerous studies have shown that VR and AR training offer superior levels of engagement and retention. [1]
Traditional medical training has been done in a similar way for hundreds of years. For example, the use of cadavers to train surgeons in an academic setting dates [2] back to the 15th century. Yet, at the same time, our medical knowledge and understanding are constantly developing.
We know much more about the human body today than we did half a millennium ago, so why is our medical training not evolving alongside it? By using advanced technology like virtual and augmented reality, we can make medical training safer for patients and medical professionals.
Why VR and AR training is advantageous for medical settings
One of the benefits of using VR-based training for medical professionals is the level of immersion it provides. Simulations in VR more accurately represent the process of an operation than working with a cadaver or mannequin.
While traditional training allows the trainee to understand the ideal progression of events, it does not accurately represent what might happen if things go wrong. Through AI-powered models, simulations can react in real time to the trainee’s decision-making, and haptic feedback can allow them to actually feel the process as if it were hands-on.
But what about other emergency scenarios that don’t involve surgery? Cadavers allow trainees to practice surgery but aren’t a practical solution for different forms of treatment. Because VR can realistically simulate more situations, it enables trainees to prepare for more scenarios than traditional training could. While it’s not possible to be ready for every circumstance that will arise, VR simulations can allow medical professionals to get less caught off guard in an emergency scenario.
Of course, training in virtual reality is significantly less risky than training on live patients. While surgeons typically get extensive experience on cadavers before they ever step foot in an actual operating room, other doctors may get their training by shadowing or being supervised by more experienced doctors. Allowing these doctors to train in virtual reality before ever interacting with real patients can ensure they are ready for the hospital floor.
Furthermore, VR training allows greater levels of repetition than traditional training methods. Medical cadavers are costly, not to mention ethically challenging. Doctors who want to repeat training to feel more confident in their abilities can do so in virtual reality without worrying about expense or waste. VR allows trainees to learn at their own pace, allowing learners to become more comfortable before venturing into the real world, and we want our doctors and surgeons to feel comfortable, after all.
Because of these benefits, VR and AR are the future of training in the medical industry. By immersing learning surgeons and emergency physicians in realistic simulations that provide them a safer, more comfortable environment in which they can learn, we are creating a group of more prepared, more confident medical professionals.
References:
-
Enhancing learning and retention with distinctive virtual reality environments and mental context reinstatement – NPJ Science of Learning
- Human cadaveric dissection: a historical account from ancient Greece to the modern era – National Library of Medicine